|
Capsule-Sized Leadless Pacemakers May Lead the Way in Heart Rhythm Management
New Generation of Cardiac Pacemakers Will Be Delivered via Catheter Directly into Atrium
|
 |
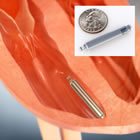
St. Jude's Nanostim leadless pacemaker |
February 9, 2014 -- Is the future of implantable pacemakers a miniaturized leadless capsule, no bigger than a coin, delivered non-surgically via a catheter, much like a stent during angioplasty?
Looking at the recent news from two of the leading manufacturers of pacemakers, one would conclude in the affirmative.
Last week, St. Jude Medical announced the first U.S. implantation of their leadless Nanostim pacemaker (press release below) at Mt. Sinai Hospital in New York. The device was implanted by Mt. Sinai's Director of Cardiac Arrhythmia Service, Dr. Vivek Reddy, who was involved with Nanostim, the privately-owned Canadian medical start-up that developed this technology and was acquired by St. Jude in October 2013 (he held significant stock options in the firm).
The clinical timeline, after initial development, started with the first-in-human implants of the Nanostim, performed in Prague in December 2012. Less than a year later, the device garnered the CE Mark and the first post-approval implant occurred in Germany in December 2013. Last week, the first investigational implant was performed in the U.S.
The Nanostim is currently available for sale in Europe but not in the U.S. where it remains an investigational device, being studied in the LEADLESS II Trial.
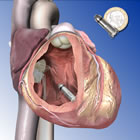
Medtronic's Micra pacemaker (compared to Euro coin, upper right) |
The next-in-line challenger to St. Jude is Medtronic, who announced the first human implant of its leadless Micra catheter in December. The third major U.S. device company in the pacing field, Boston Scientific, showed a prototype leadless capsule at the Heart Rhythm Society annual meeting in May 2013, but has yet to implant one.
This new class of pacemakers all shares various characteristics: they resemble a small battery and, in fact, are comparable in size to a AAA cell. Invariably they are compared in size to a coin. In the graphic to the right, Medtronic shows the Micra next to a Euro. St. Jude displays its Nanostim next to a U.S. quarter (above), although in its European marketing literature, the Euro is used. Boston Scientific went with a dime for their prototype (not shown).
The advantages of these leadless devices are also similar. They are, obviously, leadless; this is a critical difference from current pacemakers which require electrical leads to connect the device to the heart muscle. These leads occasionally have been the nexus for problems of corrosion, or shorting of contacts, etc. that have plagued pacemakers.
Additionally, these wireless devices do not require a surgical implant; they are delivered via catheter, snaked through the femoral vein into the right atrium. Procedure times seem to be around a half-hour.
These first generation devices will no doubt be superceded by smaller devices which require less than the 18F sheath, longer battery life, and less discomfort for the patient. Andreas Gruentzig, the inventor of coronary angioplasty, referred to the circulatory system as the body's "highway," and in the past three decades many therapies and devices have used this highway to deliver therapy to patients. These pacemakers are the latest in that cohort.
This press release from St. Jude Medical follows:

St. Jude Medical Announces First US Patient Implant of Non-Surgical, Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker
Commencement of LEADLESS II clinical research trial represents important milestone in bringing transformational pacing technology to U.S. patients
February 6, 2014 -- St. Paul, Minnesota -- St. Jude Medical, Inc. (NYSE:STJ), a global medical device company, today announced the first U.S. implant in the company's LEADLESS II pivotal trial designed to evaluate the Nanostim™ leadless pacemaker for U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval. The world's first retrievable, non-surgical pacemaker was implanted at The Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City by Dr. Vivek Reddy.
The Nanostim leadless pacemaker is designed to be placed directly in the heart without the visible surgical pocket, scar and insulated wires (called leads) required for conventional pacemakers. Implanted via the femoral vein with a steerable catheter, the device offers physicians the same pacing therapy through a less-invasive approach as compared to traditional pacemaker procedures that require more extensive surgery. The device is designed to be fully retrievable, so that it can be readily repositioned throughout the implant procedure and later retrieved if necessary.
"This clinical research trial will be testing the latest innovative, non-surgical pacemaker option for U.S. patients experiencing heart rhythm issues," said the study's co-investigator Dr. Vivek Reddy, Director of Electrophysiology Services at The Mount Sinai Hospital and Chairman of the Steering Committee of the study. "This new-age, tiny pacemaker may ultimately be safer for patients because it doesn't have leads or have to be inserted under the skin of a patient's chest, like a traditional cardiac pacemaker. I believe this pioneering, compact device, which is placed directly inside the heart, may be a true game-changing technology in cardiovascular medicine and may help revolutionize care for patients with arrhythmias. I look forward to the results of the LEADLESS II clinical trial."
The Nanostim leadless pacemaker is less than 10 percent the size of a conventional pacemaker and is the least invasive pacing technology available today. The small size of the device and lack of a surgical pocket, coupled with the exclusion of a lead, improves patient comfort and may reduce complications, including device pocket-related infection and lead failure. The elimination of the visible lump and scar at a conventional pacemaker's implant site, in addition to the removal of patient activity restrictions that are routinely put in place in an attempt to prevent dislodgement or damage to a conventional lead, will potentially improve the quality of life for patients with this technology by allowing most to continue living active, uninhibited lifestyles. The device is supported by the St. Jude Medical Merlin™ Programmer, which is also used to interrogate and program the company's other pacemakers and implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs).
"Since the introduction of the first implantable pacemaker in 1958, pacemaker technology has continued to evolve into smaller, more efficient devices," said Dr. Mark D. Carlson, chief medical officer and vice president of global clinical affairs for St. Jude Medical. "Despite this evolution, pacing technology has, until now, required surgery in addition to leads that connect the pacemaker to the heart. The Nanostim leadless pacemaker is the first miniaturized device that removes the need for leads, thus offering less invasive and less complicated procedures for physicians and patients around the world. We believe the innovative nature of this technology will change the future landscape of cardiac rhythm management devices by revolutionizing the delivery methods and design of these life-saving technologies."
Cardiac pacemakers are used to treat bradycardia, which is a heart rate that is too slow. These devices monitor the heart and provide electrical stimulation when the heart beats too slowly for each patient's specific physiological requirements. More than 4 million people worldwide have an implanted pacemaker or other cardiac rhythm management device, and an additional 700,000 patients receive the devices each year.
LEADLESS II Clinical Trial Design
The LEADLESS II pivotal trial is a prospective, non-randomized, multi-center, international clinical research trial designed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the Nanostim leadless pacemaker in patients indicated for the device. It is being conducted under an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) from the FDA, and will enroll approximately 670 patients at 50 centers in the U.S., Canada and Europe.
LEADLESS Clinical Trial Preliminary Results
Initial results from the LEADLESS study, a prospective, single-arm, multicenter study evaluating patients with the Nanostim leadless pacemaker, were presented last year and demonstrated overall device performance comparable to conventional pacemakers. Total implant procedure times averaged 28 minutes. Even with miniaturization, the device battery is expected to have an average lifespan of more than nine years at 100 percent pacing, or more than 13 years at 50 percent pacing.
The Nanostim pacemaker received CE Mark approval in 2013 and is available in select European markets. The device is not available for sale in the U.S.
About St. Jude Medical
St. Jude Medical is a global medical device manufacturer dedicated to transforming the treatment of some of the world's most expensive, epidemic diseases. The company does this by developing cost-effective medical technologies that save and improve lives of patients around the world. Headquartered in St. Paul, Minn., St. Jude Medical has four major clinical focus areas that include cardiac rhythm management, atrial fibrillation, cardiovascular and neuromodulation. For more information, please visit sjm.com or follow us on Twitter @SJM_Media.
Forward-Looking Statements
This news release contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 that involve risks and uncertainties. Such forward-looking statements include the expectations, plans and prospects for the Company, including potential clinical successes, anticipated regulatory approvals and future product launches, and projected revenues, margins, earnings and market shares. The statements made by the Company are based upon management's current expectations and are subject to certain risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements. These risks and uncertainties include market conditions and other factors beyond the Company's control and the risk factors and other cautionary statements described in the Company's filings with the SEC, including those described in the Risk Factors and Cautionary Statements sections of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 29, 2012 and Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarter ended September 28, 2013. The Company does not intend to update these statements and undertakes no duty to any person to provide any such update under any circumstance.
Disclosures
Dr. Reddy receives financial compensation as a consultant and advisory board member for St. Jude Medical, the study sponsor and manufacturer of the Nanostim pacemaker system being evaluated in this study. In addition, in 2013 he received one-time financial compensation from St. Jude Medical in the form of an option buyout relating to St. Jude Medical's acquisition of Nanostim.
Reported by Burt Cohen, February 9, 2013
|


