|
Can Near-Infrared Imaging Predict Heart Attack Risk?
New Study to Enroll 9,000 Patients at 100 Sites Worldwide
|
 |
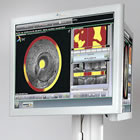
Infraredx TVC Imaging System |
February 27, 2014 -- What causes a heart attack? Is it a physical narrowing in the coronary artery, a blockage that can be seen on angiography? Or is it more likely the eruption of a lipid-rich plaque, a so-called vulnerable plaque, that may not look significant in percent stenosis during a standard catheterization?
Dr. James E. Muller, along with colleagues, Tofler and Stone, first described this "vulnerable plaque" a quarter-century ago in an article, published in Circulation, "Circadian variation and triggers of onset of acute cardiovascular disease." This paper laid the groundwork for the concept that external triggers, physical or mental, could cause a vulnerable plaque to erupt, rapidly increasing the coagulability of the platelets and causing thrombus, or clot, to grow and block the circulation, resulting in a heart attack.
As a Professor of Medicine at Harvard, Dr. Muller continued his research into ways to identify and visualize such plaques. In 1998 he founded Infraredx to investigate the ability of near-infrared spectroscopy to accomplish this. Years of development led to the company's TVC Imaging System™, which combines Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) with Near InfraRed Spectroscopy (NIRS) to assess both vessel structure and composition of plaques, and currently is the only imaging system approved by the FDA specifically for the detection of lipid core plaques.
Other studies of plaque characteristics have been done, most notably the PROSPECT Study, sponsored by Abbott and Volcano, which used Volcano's proprietary VH® IVUS tissue characterization software to measure these non-obstructive lesions. The PROSPECT investigators found that certain high-risk lesions, including those with a relatively small lumen area and a large amount of plaque, and a significant amount of dead tissue or necrosis near the lumen as identified by VH® IVUS, had an almost 20% risk of a cardiac event within three years.
PROSPECT confirmed that angiography alone did not yield sufficient information to assess whether or not a lesion was at high risk for causing a heart attack. And while the use of intravascular imaging definitely was able to delineate certain characteristics that showed increased risk, called "predictive lesions," cardiologists, such as Dr. Patrick Serruys opined that the real problem was what then to do about these lesions. Should they be stented preemptively? Could there be some adjunctive therapy that could be delivered to them to prevent rupture? Five years ago, when the PROSPECT results were first released, there were not good answers to these questions. Additionally, the classification of "predictive lesions" was not specific enough to warrant across-the-board intervention.
Fast forward to 2014. Today MedStar Heart Institute and Infraredx announced enrollment of the first patient in the Lipid-Rich Plaque (LRP) Study, which will involve 100 centers worldwide and have a target enrollment of 9,000 patients. The LRP Study is expected to take almost five years to complete, with final data collection estimated for December 2018. But, as Dr. Muller states in a company press release (reprinted below): "Once completed, the LRP Study could redefine the role of intravascular imaging and lay the groundwork for changing standard protocol for managing coronary artery disease."
This morning's press release from Infraredx follows:

MedStar Heart Institute and Infraredx, Inc Announce Enrollment of First Participant in Lipid-Rich Plaque (LRP) Study Evaluating Ability of Near-infrared Coronary Imaging to Predict Risk of Heart Attacks
February 27, 2014 -- Washington, DC, and Burlington, MA -- MedStar Heart Institute of Washington, D.C. and Infraredx, Inc., a medical device company committed to advancing the diagnosis and management of coronary artery disease, today announced the enrollment of the first participant in the Lipid-Rich Plaque (LRP) Study, a prospective, multi-center study aimed at identifying a correlation between LRPs, a particular type of fatty coronary artery plaque, and the occurrence of a cardiac event within two years. LRPs, which are implicated in most heart attacks, will be identified in study participants using the Infraredx TVC Imaging System™, a first-in-class dual modality intravascular imaging catheter.
MedStar Heart Institute, one of the 100 clinical sites worldwide to participate in the trial, is a national leader in the research, diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular disease, and consistently recognized by U.S. News & World Report and The Society of Thoracic Surgeons as one of the top heart hospitals in the nation.

James E. Muller, MD |
"We are pleased to announce the start of enrollment for this major international study testing the ability of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to detect the cholesterol-rich plaques suspected of causing heart attacks," said James Muller, MD, co-founder and chief medical officer of Infraredx. "The decision to undertake this important study was based on a wealth of data stemming from decades of research and development by a dedicated team of more than 100 engineers and clinical scientists. Once completed, the LRP Study could redefine the role of intravascular imaging and lay the groundwork for changing standard protocol for managing coronary artery disease."
The TVC Imaging System integrates NIRS to detect lipid-core plaques, and enhanced intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) to visualize the vessel structure, including the presence of plaques and the degree of stenosis (narrowing). The system identifies plaques suspected to be vulnerable to rupture, which can cause a fatal coronary blockage. Current methods of diagnosing coronary artery disease are limited in their ability to detect such plaques.
Coronary artery plaques are caused by the build-up of cholesterol and other materials inside the walls of the coronary arteries. Previous studies have demonstrated that NIRS imaging in patients can identify cholesterol-rich plaques that have caused a heart attack or cardiac arrest. In a heart attack study[1] published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology Cardiovascular Interventions, researchers used NIRS imaging to detect a lipid-rich plaque at the culprit site (site suspected to be the source of the heart attack) in 19 of the 20 patients studied. This important data was featured as one of Discover magazine's top 100 science stories of 2013.

Ron Waksman, MD |
"As a national leader in research and treatment of cardiovascular disease, MedStar Heart Institute is proud to lead and enroll the first participant in this potentially ground-breaking study," said Ron Waksman, MD, International Principal Investigator of the LRP Study, and director of Cardiovascular Research and Advanced Education at the MedStar Heart Institute. "The LRP Study could be the largest study to use intravascular imaging to link suspected vulnerable plaques to a higher risk of future coronary events. Successful identification of vulnerable plaques could help clinicians better manage high-risk patients and potentially prevent coronary events with the vast array of currently available interventional devices."
For more information on the LRP Study and enrollment sites and criteria, please visit http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02033694
About The TVC Imaging System™
The TVC Imaging System™ is a first-in-class dual-modality intravascular imaging system that holds the potential to revolutionize the management of coronary artery disease by providing information that is critical for evaluating vessel structure and composition, also known as true vessel characterization. The TVC Imaging System helps interventional cardiologists identify which patients are prone to complications during stenting. The device enables cardiologists to predict the risk of peri-procedural heart attacks by assessing not only the degree of stenosis, but also the presence and extent of lipid-core plaques (LCP).
The device is the only multimodality imaging system to combine both intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Through IVUS technology, the TVC Imaging System provides clear and relevant information about vessel structure, in real time. The TVC Imaging System is the only device specifically approved in both the U.S. and Europe for the detection of LCPs. NIRS measurements have been made in over 5,000 patients in over 100 hospitals worldwide.
About Infraredx, Inc.
Infraredx, Inc. is a privately-funded medical device company dedicated to helping provide practitioners with the information needed for enhanced clinical decision making in treating coronary artery disease. The company is committed to improving the safety and efficacy of coronary stenting and ultimately serving as part of a strategy to prevent initial coronary events.
Through its TVC Imaging System™, Infraredx is changing the way coronary artery disease is diagnosed and treated. The TVC Imaging System is the only intravascular imaging system that enables true vessel characterization through simultaneous structural and compositional imaging data obtained in a single pullback. Founded in 1998, Infraredx is headquartered in Burlington, Mass. For more information, visit www.infraredx.com.
About MedStar Heart Institute
MedStar Heart Institute, headquartered at MedStar Washington Hospital Center in Washington, D.C., is a national leader in the research, diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular disease, and has been the premier destination for cardiac care in the nation's capital for more than 50 years. Consistently recognized for excellence by U.S.News & World Report and The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, MedStar Heart Institute entered into a first-of-its-kind clinical and research alliance with world-renowned Cleveland Clinic Sydell and Arnold Miller Family Heart & Vascular Institute in January 2013. Uniting two of the nation's top heart programs, this alliance enhances the Baltimore-Washington metropolitan region's access to advanced, innovative cardiac care and research. MedStar Heart Institute comprises more than 100 cardiac physician specialists throughout the mid-Atlantic region, as well as the nationally recognized heart care of MedStar Washington Hospital Center, the academic depth of MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, and the cardiac services of MedStar Montgomery Medical Center, MedStar Union Memorial Hospital, MedStar St. Mary's Hospital and five other acute care hospitals.
[1] Madder et al, JACC Interventions 2013)
Reported by Burt Cohen, February 27, 2014
|




