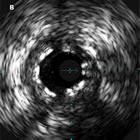
For the interventionalist, proper sizing of coronary stents is critical. While imaging via angiography has been the standard for years, newer intravascular imaging technologies, such as IVUS and OCT, are becoming more widely used, as evidence accrues that these modalities make a difference in outcomes. For example, IVUS (Intravascular Ultrasound) not only allows the measurement of the exact open diameter of the vessel, as seen on angiography, but it shows the “invisible to angiography” layer of plaque. plaque that will be compressed, so that a more accurate post-PCI diameter can be determined. Under-expanded stents have been associated with increased stent thrombosis and restenosis. Continue reading
Category Archives: Stent Thrombosis
Post-Dilatation Stent Sizes
Filed under Angiograms, Drug-Eluting Stents, Imaging, IVUS, OCT, Stent, Stent Thrombosis
Status of the “Disappearing Stent” in Europe: It’s Complicated!
 Last night news began circulating on Twitter that Abbott’s Absorb BVS (Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold) was being withdrawn from the European market. This information was prompted by several physicians posting on Twitter a March 31 “Urgent Field Safety Notice/Physician Advisory” letter from Abbott addressed to “Valued Abbott Vascular Customer.”
Last night news began circulating on Twitter that Abbott’s Absorb BVS (Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold) was being withdrawn from the European market. This information was prompted by several physicians posting on Twitter a March 31 “Urgent Field Safety Notice/Physician Advisory” letter from Abbott addressed to “Valued Abbott Vascular Customer.”
A number of news sources, including this one, posted articles and tweets to the effect that the Absorb was being taken off the commercial markets and, as the letter stated, “Effective May 31, 2017, the device will only be available in clinical register setting at select sites/institutions that will play a pivotal role in the monitoring of this technology until Summer 2018 at which time the situation will be reviewed.”
This morning Abbott reacted to this initial flurry of reports that they had “pulled the Absorb” with some clarification: specifically that the Absorb is NOT being pulled from the market and still retains the CE Mark. An Abbott spokesperson told Angioplasty.Org, “Absorb will continue to be commercially available in Europe through the registries.”
But the relationship, as they say on Facebook, is complicated.
Can Using IVUS (Intravascular Ultrasound) Prevent Stent Thrombosis?
A recent paper, published online before print in SCAI’s journal, Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, yet again adds to the evidence that intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) imaging during PCI can improve stent placement and expansion in a way that may prevent stent thrombosis (ST).
Titled, “Angiographically confirmed stent thrombosis in contemporary practice: insights from intravascular ultrasound“, the study looked at five years (2005-2010) of a multicenter registry of stent thromboses and studied the IVUS images where performed. Continue reading
Filed under Innovators, IVUS, Japan, Stent Thrombosis
Plavix After Stents: How Long?

Dr. Eric Topol
I recently interviewed Dr. Eric Topol for Angioplasty.Org about current efforts to determine the optimal duration of dual antiplatelet therapy (a.k.a. DAPT or clopidogrel plus aspirin) after drug-eluting stent placement. My first question was what had we learned about this issue since the 2006 FDA stent safety hearings? And his answer was “Unfortunately, we don’t know anything more…“.
Sort of shocking. A major study was supposed to come out of those hearings, but the DAPT study just began recruiting last summer and won’t be completed for four years. This massive study, sponsored by all the major stent makers, as well as the manufacturers of antiplatelet meds, will enroll 20,000 patients and test them at 12 and 30 months to determine the rates of MACCE (death, heart attack and stroke) stent thrombosis and major bleeding complications. It will be performed with all drug-eluting stent brands and will not compare one to another. What will this teach us? Dr. Topol has an opinion about the DAPT study:
“The notion that we should treat all patients for X duration is totally crazy. It completely goes against all the evidence that every patient is an individual with a separate biologic story, and a risk of bleeding. And then there is obviously a big expense. The drug companies would love it to be 30 months or 30 years. But to try to generalize from a trial like that, I’m amazed that it’s going forward.”
Dr. Topol (who, by the way, was an invited panel member at those 2006 FDA hearings) is currently Director of the Scripps Translational Science Institute (STSI) where he is conducting research on the genomics of coronary artery disease. The bottom line is that all patients are not the same — and they respond to antiplatelet therapy differently. So Dr. Topol believes that the “one-size-fits-all” concept of thrombosis prevention just doesn’t apply.
Another concept is that all drug-eluting stents aren’t the same. Because of the metal structure, polymer coating or drug itself, each device has different characteristics and different healing properties. This was seen clearly in the ODESSA trial, where Dr. Giulio Guagliumi used OCT intravascular imaging to measure stent coverage at six months. He found significant incomplete coverage in the CYPHER and TAXUS stents, but complete healing in the ENDEAVOR.
As a result of these findings and other clinical data, two trials, involving only Medtronic’s ENDEAVOR stent, are currently starting up: SEASIDE, which Dr. Topol is involved in, will measure the outcomes of patients who receive and only get six months of DAPT; and OPTIMIZE, being conducted in Brazil by Dr. Fausto Feres, which is stopping DAPT at three months.
Rather than testing if DAPT is more effective at longer durations, such as 12 and 30 months, these studies are testing to see if it is just as effective at shorter periods, when used with a DES that has a greater healing profile, like the ENDEAVOR. The advantages of a shorter DAPT duration are several:
- less risk of bleeding complications (inherent in the use of antiplatelet drugs);
- less cost (Plavix costs $4/day — the difference of a year or two is significant — newer antiplatelet drugs like prasugrel cost even more);
- less problems deferring surgery (in order to perform surgery of any sort, for example knee replacement, etc., antiplatelet therapy must be stopped).
The short back story here is that when drug-eluting stents first came on the market in 2003-2004, the FDA recommended six months of DAPT to keep the blood from clotting in and around the stent (a.k.a. stent thrombosis). Within a couple of years, reports surfaced about a small number of patients who suffered late stent thrombosis (six months or more after stenting). A flurry of concern arose and the 2006 FDA stent safety hearings resulted in recommendations to extend DAPT to 12 months or more — the current guidelines. But, as Dr. David Kandzari, co-principal investigator for the SEASIDE trial told Angioplasty.Org:
“Current treatment guidelines are based principally on consensus opinion and intuition rather than hard evidence that extending DAPT reduces the risk of late and very late ST. In fact, in more recent trials, patients experiencing very late ST are more commonly on DAPT than off.”
Dr. Kandzari explores this issue in detail in his Viewpoint article in December’s JACC: Interventions, “Identifying the ‘Optimal’ Duration of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Drug-Eluting Stent Revascularization”
For more information, read my interview with Dr. Topol and keep up with the latest news in our StentCenter.


 At this week’s annual European Society of Cardiology Congress in Rome, an important randomized clinical trial on stents was presented by Professor Kaare H. Bønaa, MD, PhD of the Clinic for Heart Disease, St. Olav’s University Hospital in Trondheim, Norway. Called NORSTENT, short for the “Norwegian Coronary Stent Trial,” this was the largest stent trial ever conducted, with 9,013 patients followed for six years. That’s serious!
At this week’s annual European Society of Cardiology Congress in Rome, an important randomized clinical trial on stents was presented by Professor Kaare H. Bønaa, MD, PhD of the Clinic for Heart Disease, St. Olav’s University Hospital in Trondheim, Norway. Called NORSTENT, short for the “Norwegian Coronary Stent Trial,” this was the largest stent trial ever conducted, with 9,013 patients followed for six years. That’s serious!  No one thought it would take quite so long to get this information, but in just a couple hours results from
No one thought it would take quite so long to get this information, but in just a couple hours results from